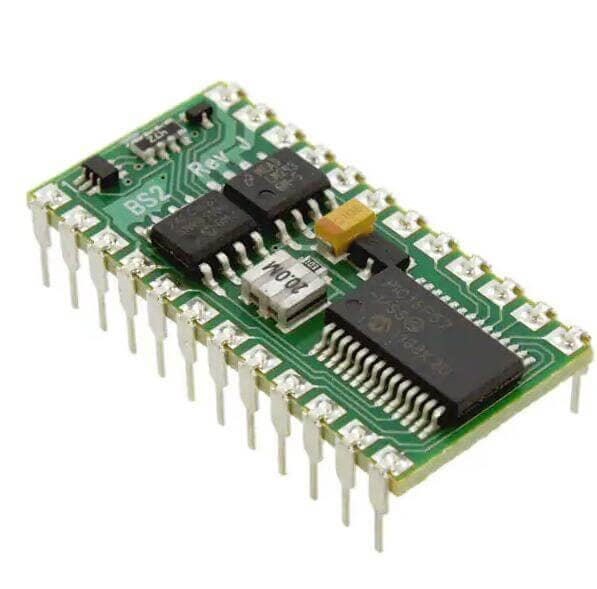
Metal Substrate PCB
- Metal Substrate PCB Introduction
- Metal Substrate PCB Definition
- Metal Substrate PCB Application
- Aluminum PCB Characteristic
- Aluminum PCB Classification
- Aluminum PCB Materials : T-preg & T-lam Properties, Application of materials, Supply Specification
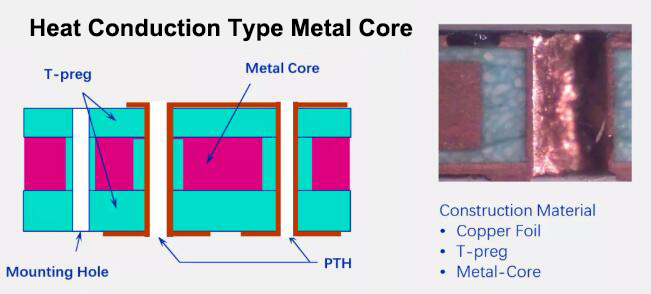
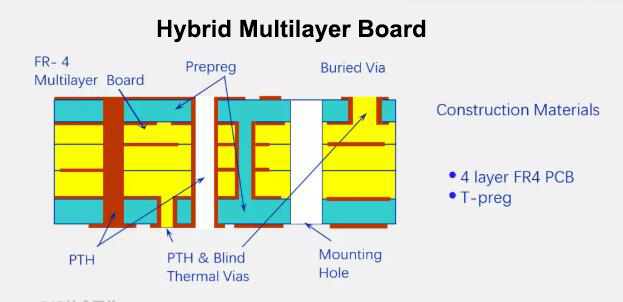
- Metal Substrate PCB Structural Style
Metal Substrate PCB Introduction
1. In the 1960s and 70s, the Ministry of International Trade and Industry of Japan conducted a lot of investigations, and recognized that the problem faced by PCB use is high-density assembly, high assembly density of components and heat dissipation are a big problem. Ordinary paper, glass cloth, and epoxy copper clad laminates are insulating materials with low thermal conductivity and are not suitable for heat dissipation. When there are many layers, high density, and high power, the heat must not be removed. Therefore, a metal-based printed board must be used.
2. It was pioneered in the United States in 1963, and the American Ves lerm Electrico company made iron-based sandwich printed boards. Application on the relay.
3.In 1969, Japan’s Sanyo company first invented the manufacturing technology of aluminum-based copper clad laminates, and began to apply to STK series power amplifier hybrid integrated circuits in 1974.
4. In the 1980s and 1990s, metal substrates were widely used in countries around the world. Among the metal PCB substrates, aluminum-based copper clad laminates had the largest market consumption. In 2004, the output value of aluminum-based copper clad laminates in Japan reached more than 1.70 billion dolla
Metal Substrate PCB Definition
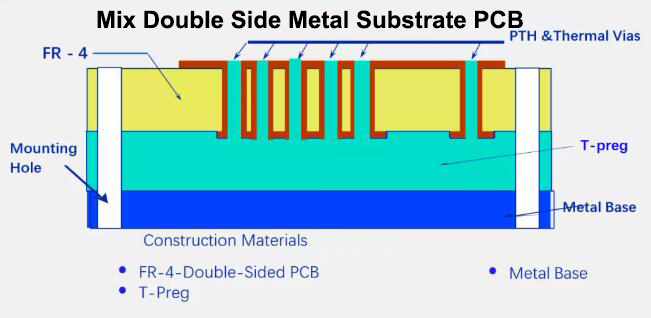
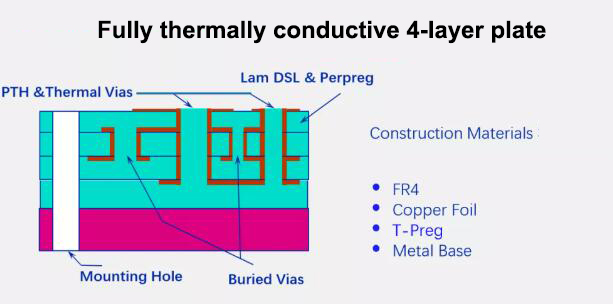
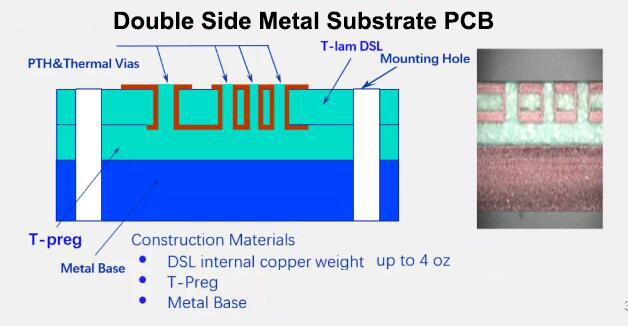
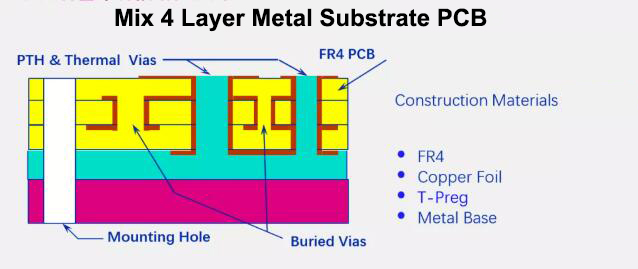
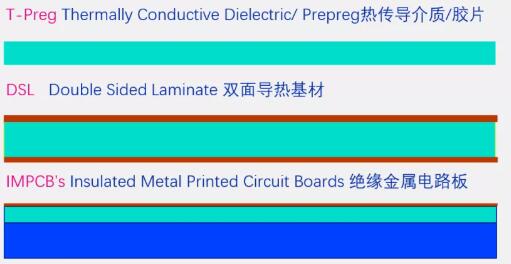
The metal substrate is a unique metal-based copper clad laminate (see the structure diagram).

The metal-based printed circuit board is mainly used in electrical appliances with heat dissipation requirements for the terminal product. It is a composite printed circuit board made of a trinity of a metal substrate, an insulating dielectric layer and a circuit copper layer. The commonly used metals are aluminum, iron, copper, steel, tungsten-molybdenum alloy, and aluminum-based copper clad laminates are the most common, and the insulating dielectric layer is usually modified epoxy resin, polyphenylene ether (PPO), polyimide (PI), PTFE+ Ceramic fillers, etc. Aluminum-based copper clad laminate(Aluminum PCB) has excellent heat dissipation, electromagnetic shielding, and dimensional stability.
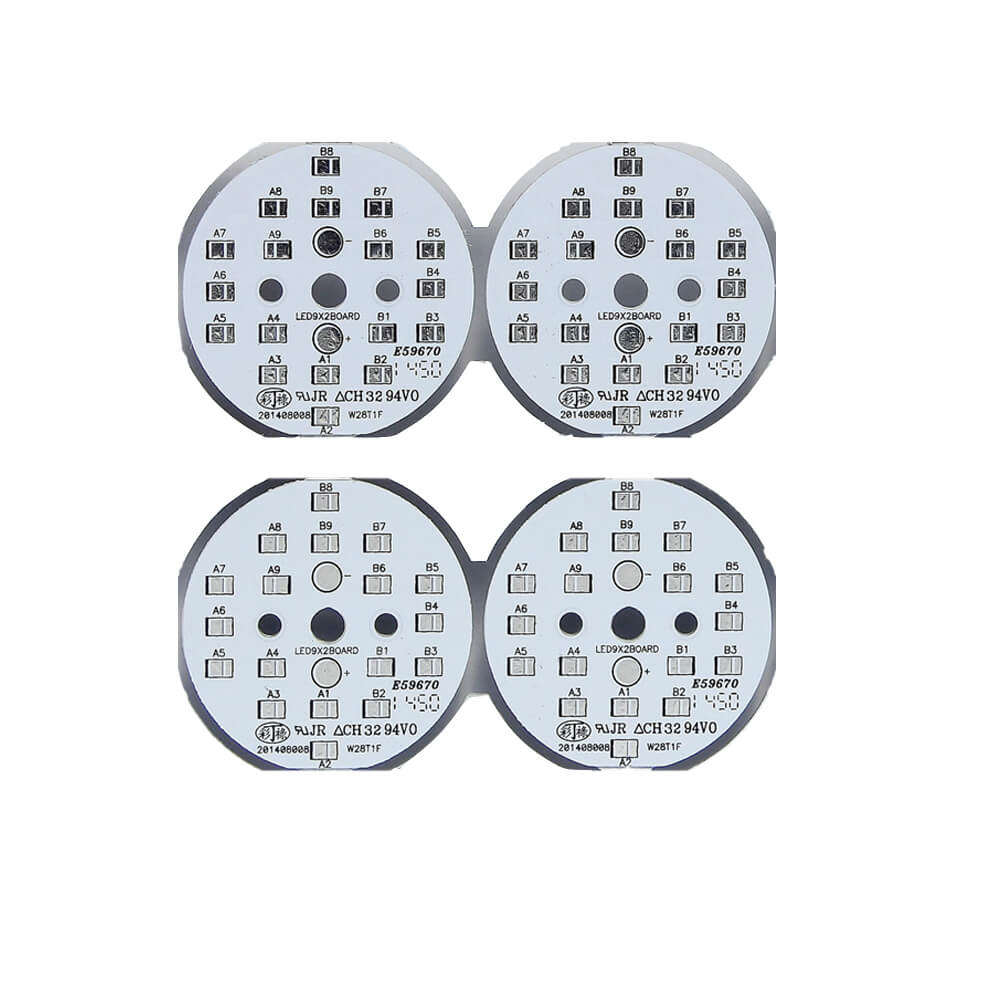
Metal Substrate PCB Application
Metal-based printed boards are mainly used in electrical appliances that require heat dissipation in terminal products.

- Iron-based copper clad laminates and silicon steel copper clad laminates have excellent electrical properties, magnetic permeability, pressure resistance, and high substrate strength. Mainly used for brushless DC motors, tape recorders, main shaft motors and intelligent drives for tape recorders. However, the magnetic properties of silicon steel copper clad laminates are better than iron-based copper clad laminates.
- Copper-based copper clad laminate has the basic performance of aluminum-based copper clad laminate, and its heat dissipation is better than aluminum-based copper clad laminate. This kind of substrate can carry large current and is used to make PCBs for high-power circuits such as power electronics and automotive electronics. The high density, high value, and easy oxidation of the substrate limit its application, and the amount is much lower than that of aluminum-based copper clad laminate.
- Aluminum-based copper clad laminates have excellent electrical properties, heat dissipation, electromagnetic shielding, high withstand voltage and bending properties, and are mainly used in automobiles, motorcycles, computers, home appliances, communication electronic products, and power electronic products.
- Among the metal PCB substrates, aluminum-based copper clad laminates have the largest market usage, mainly used in high-brightness LEDs (lighting and LCD backlight modules), output amplifiers, equalization amplifiers, preamplifiers, transistor bases, solid state relays, and electrical appliances: Power supply devices, power supplies, DC transformers, automotive electrical modules, etc.
Aluminum PCB Characteristic
- Substrate material: high thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion.
- Dielectric materials: sufficient strength, low thermal expansion, high thermal conductivity, high temperature resistance.
- Joining technology of aluminum plate and dielectric layer: (Peel strength> 10 lb/inch or more).
4. Low thermal damping interface material. - The matching of thermal expansion coefficients between dissimilar materials.
Aluminum PCB Classification
- General-purpose aluminum-based copper clad laminate: the insulating layer is composed of epoxy glass cloth bonding sheet.
- High heat dissipation aluminum-based copper clad laminate: the insulating layer is composed of high thermal conductivity epoxy resin or other resin.
- Aluminum-based copper clad laminates for high-frequency circuits: The insulating layer is made of polyene resin or polyimide resin glass cloth bonding sheet.
The biggest difference between aluminum PCB and conventional FR-4 PCB lies in heat dissipation. Compared with aluminum-based PCB with a thickness of 1.5mm, FR-4 PCB have a thermal resistance of 20 to 22 ℃, and the thermal resistance of the latter 1.0 to 2.0. ℃, the latter is much smaller.
Aluminum PCB Materials
ITEQ aluminum substrate for example
The T-pregTM system
T-preg (thermal conductive film): it is the core of T-lam (aluminum substrate) and has three main functions.
1. Heat conduction function
2. Electrical insulation function
3. Interlayer bonding function
The T-lamTM System
T-preg & T-lam Properties | ||
Item | ITEQ T-Preg FR-4 | ITEQ-Laird 1KA |
| Thermal conductivity (w/m·k) | 0.4 | 3 |
| Insulation breakdown voltage (V /mil) | 600 | 800 |
| Dielectric constant (DK) | 4.3 | 4.2 |
| Are there reinforcements | Yes | Yes |
| Peel strength (Ib/in) | ~6 | ~6 |
| UL combustion class | 94V-0 | 94V-0 |
| Maximum operating temperature ℃ | 130 | 130 |
Application of materials | |||
Product Category | Thermal Conductivity | Characteristic | Application Area |
ITEQ FR-4 | 0.4W | Reinforced materials, large thermal resistance, 2.2 ° C / W. The thermal conductivity is not very good. | Low end led. Like a flashlight. |
ITEQ-univacco SA | 1W | No reinforcement, low thermal resistance, 0.4 ° C / W. Good heat dissipation, excellent dimensional stability, good machinability and excellent cost performance. | Middle and low end led, audio equipment, transistor base, power electronics, high current and high power circuits. |
ITEQ-unicacco SK | 2~3W | No reinforcement, low thermal resistance, 0.2 ° C / W. Good heat dissipation, excellent dimensional stability, good machinability and excellent cost performance. | High end led, power control module, automotive electronics high current, high power circuit, solid state relay. |
ITEQ-Laird 1KA | 3W | Reinforced material, low thermal resistance, 0.35 ° C / W. Good heat dissipation, excellent dimensional stability and good machinability. | High end led, power control module, automotive electronics, high current, high power circuit, electrical appliances in harsh environment. |
Supply Specification
Product specification
1. Cu : H~6 oz
2. Thermal conductive P / P dielectric material: 3 ~ 12 mil.
3. Metal aluminum plate: 1050, 5052, 6061, 1050 – 99.9% aluminum, industrial aluminum, applied to low-end products; 5052 aluminum magnesium alloy, applied to low-end products.
4. 6061 aluminum magnesium silicon alloy is applied to high-end products, such as Emerson Emerson and Huawei.
5. Protective film on aluminum base: PL – resistant to 300C, used for tin spraying; pet – resistant to 150C, used for gold and silver precipitation; pet – resistant to 80C, used for general protection.
T-lam size
1. 460mm × 600mm (refers to Laird material)
2. 500mmx600mm
Product type
1. Single side
2. Double and multilayer
3. Metal core
Metal Substrate PCB Structural Style