Soldering is an important step in the production of electronic equipment. After soldering, there are always varying degrees of flux residues and other types of contaminants on the circuit board surface, even if a low-solid content, halogen-free, no-clean flux is used. There will still be more or less residue. In order to prevent circuit failure due to corrosion, cleaning must be performed after welding to ensure the reliability, electrical indicators, and working life of electronic equipment. Since military products must be cleaned, the cleaning process is particularly important for military products.
The traditional method of cleaning printed circuit boards is to use organic solvents. A mixed organic solvent composed of CFC-113 and a small amount of ethanol (or isopropyl alcohol) has a good cleaning ability for the residue of rosin flux, but due to the CFC-113 113 has a destructive effect on the atmospheric ozone layer and has been banned from use. The currently available non-ODS cleaning processes include water-based cleaning, semi-aqueous cleaning, and solvent cleaning. In addition, no-cleaning processes without cleaning can also be used. Last article we have introduced the PCB water-based cleaning, next we will introduce the Semi-aqueous cleaning.
Semi-aqueous Cleaning
Semi-aqueous Cleaning Agent
The components of semi-aqueous cleaning agents generally include organic solvents and surfactants. For example, the EC-7 semi-aqueous cleaning agent, first used in printed circuit board cleaning, comprises terpene hydrocarbon solvents and surfactants. Most semi-aqueous cleaning agents also contain water in their formulas. Still, due to the large water content (only 5%-20%), semi-aqueous solvents appear to be transparent and uniform like solvent cleaning agents solution. Unlike general solvent cleaning agents, the organic solvent used in semi-aqueous cleaning agents has a relatively high boiling point. Hence, it is low in volatility and does not need to be cleaned in a closed environment like solvent cleaning agents, and the cleaning agent does not need to be replaced frequently during the cleaning process. Just replenish the cleaning dosage appropriately. The organic solvents used in preparing semi-aqueous cleaning agents for cleaning printed circuit boards mainly include terpene and petroleum hydrocarbon solvents, glycol ethers, N-methylpyrrolidone, etc. When selecting the solvent type, the solvent type should be selected according to the printed circuit board. Specific conditions include the contamination of raw materials such as circuit boards and electronic components and the type of flux used during welding.
Semi-aqueous Cleaning Process
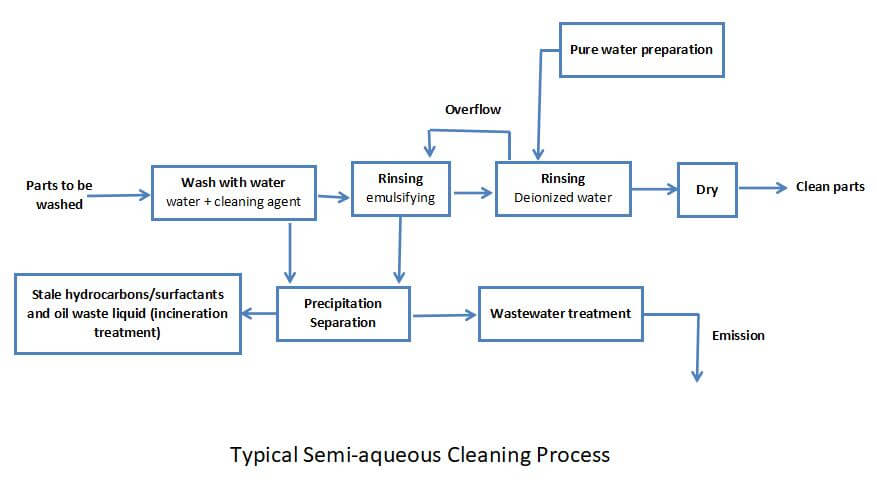
The semi-aqueous cleaning process also includes cleaning, rinsing, and drying. The cleaning process is often combined with ultrasonic cleaning to improve the cleaning effect and reduce cleaning time. Since using ultrasonic waves will increase the temperature of the cleaning agent, care must be taken to control the cleaning temperature strictly. The flash point of the cleaning fluid must not be exceeded (generally the cleaning temperature is controlled below 70°C). An emulsification recovery tank is added between the cleaning and rinsing processes, and the organic solvent concentration in the semi-aqueous cleaning solution is very high. After cleaning, there will still be more cleaning solutions on the surface of the printed circuit board. If cleaned, The printed circuit board is directly placed into the water rinse solution. The organic solvent stained on the surface of the printed circuit board will pollute the rinse water, greatly increasing the load of the subsequent water treatment process and the load between the cleaning and rinsing processes. An emulsion recovery device containing an emulsifier water solvent can strip the organic solvent on the surface of the printed circuit board from the surface of the printed circuit board through emulsification and dispersion, and filtering can be used in this emulsion recovery device. The machine and oil-water separation device separate and recover organic solvents and dirt deposits. Since there is very little organic solvent on the surface of the printed circuit board entering the rinsing tank, it reduces the load of the rinsing process and the load of wastewater treatment. Then rinse with deionized water 2-3 times to remove the dirt. Since semi-aqueous cleaning uses water as a rinsing agent, it has the same difficulty in drying as water-based cleaning, and similar measures need to be taken to increase the drying speed.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Semi-aqueous Cleaning Process
The advantages of the semi-aqueous cleaning process are:
- It has strong adaptability to various welding processes, so there is no need to change the original welding process when using the semi-water cleaning process;
- Its cleaning ability is relatively strong and can remove water-soluble dirt and oil stains at the same time;
- Good compatibility with most metal and plastic materials. It is less volatile than solvent cleaning agents and evaporates during use, resulting in less loss.
The disadvantages of the semi-aqueous cleaning process are:
- There are the same problems as water-based cleaning that require using pure water for rinsing, difficulty in drying, and large amounts of wastewater treatment.
- The semi-aqueous cleaning process requires a large site and space, and the one-time investment in equipment is relatively large, especially for online cleaning machines.
- Since semi-aqueous cleaning agents contain more organic solvents, safety measures such as protection against toxic solvents and fire and explosion protection must be added.
- Furthermore, semi-aqueous cleaning agents cannot be recycled and reused through distillation like solvent cleaning agents, so the cost is higher.