PCB exposure means that under UV irradiation, the photoinitiator absorbs light energy and decomposes into free radicals, which then lead to the polymerization and crosslinking reaction of luminescent polymerized monomers. After the reaction, a large molecular structure insoluble in dilute alkali solution is formed. Exposure is generally carried out in the automatic double-sided exposure machine. Now the exposure machine can be divided into air-cooled and water-cooled according to the cooling mode of the light source.
How to Correctly Determine The PCB Exposure Time?
Due to the different exposure machines used by various manufacturers of dry film, i.e. different light sources, lamp power and lamp distance, it is difficult for dry film manufacturers to recommend a fixed exposure time for PCB. Foreign companies producing dry film have their own special or recommended optical density ruler. When the dry film leaves the factory, the recommended imaging level is marked. China’s dry film manufacturers do not have their own special optical density ruler. Riston grade 17 or Stouffer grade 21 optical density ruler is usually recommended.
The optical density of the first stage of the Riston grade 17 optical density ruler is 0.5, and then each stage increases with the optical density difference ad of 0.05, and the optical density of grade 17 is 1.30. The optical density of the first stage of stuffy 2L level optical density ruler is 0.05, and then each stage increases with the optical density difference △ D of 0.15 to 3.05 at 2L level. When exposed with an optical densitometer, for the grades with low optical density (i.e. more transparent), the dry film receives more UV energy and the polymerization is more complete, while for the grades with high optical density (i.e. less transparent), the dry film receives less UV energy, does not polymerize or the polymerization is incomplete, and is displayed or left only a part during development. In this way, different imaging stages can be obtained by selecting different time for exposure. The usage of Riston grade 17 densitometer is briefly introduced as follows: a. the drug film is downward during exposure; b. Put the film on the copper-clad laminate for 15 minutes before exposure; c. Place for 30 minutes after exposure. Select any exposure time as the reference exposure time, expressed in TN. the maximum number of stages left after development is called the reference number. Compare the recommended number of stages with the reference number, and calculate according to the coefficient table below.
Series Difference | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
Coefficient K | 1.122 | 1.259 | 1.431 | 1.585 | 1.778 | 2.000 | 2.239 | 2.512 | 2.818 | 3.162 |
When the use stage needs to be increased compared with the reference stage, the exposure time of the use stage T = KTR. When the use stage needs to be reduced compared with the reference stage, the exposure time of the use stage T = TR / K. In this way, only one test can determine the optimal exposure time. It can also be observed by experience without optical density ruler. The appropriate exposure time can be determined by gradually increasing the exposure time according to the brightness of the developed dry film, whether the image is clear, whether the image linewidth is consistent with the original negative, etc.
Strictly speaking, it is unscientific to measure exposure by time, because the intensity of the light source often changes with the fluctuation of external voltage and the aging of the lamp. The formula defined by light energy E = it, where e represents the total exposure, and the unit is MJ / cm2; I is the intensity of light, in milliwatts per square centimeter; T is the exposure time, in seconds. As can be seen from the above formula, the total exposure e varies with light intensity I and exposure time t. When the exposure time t is constant, the light intensity I changes and the total exposure also changes. Therefore, although the exposure time is strictly controlled, the total exposure accepted by the dry film at each exposure is not necessarily the same, so the degree of polymerization is different. In order to make the energy of each exposure the same, an optical energy integrator is used to measure the exposure. The principle is that when the light intensity I changes, the exposure time t can be automatically adjusted to keep the total exposure e unchanged.
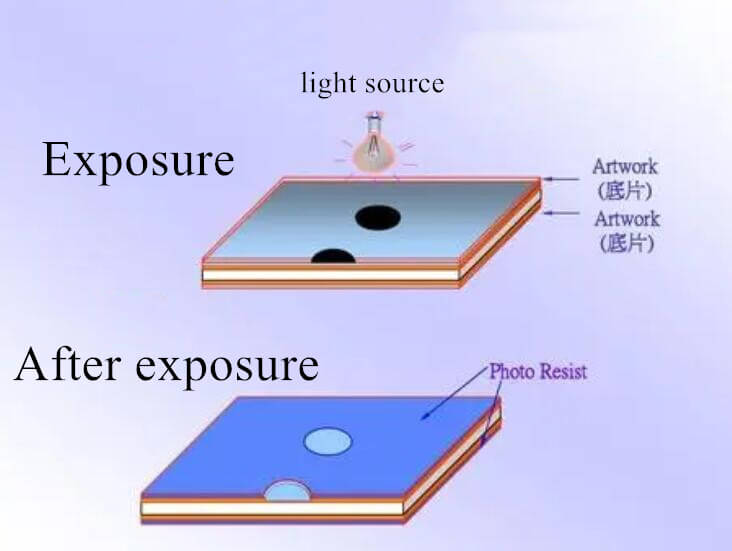
PCB Exposure Positioning
1) Visual positioning
Visual positioning is usually applicable to the use of diazo base plate, which is in a brown or orange translucent state; However, it is not transparent to UV} light. The bonding pad of the base plate is overlapped and aligned with the hole of the printed board through the diazo image, and the exposure can be carried out by fixing it with adhesive tape.
2)The off pin positioning system
The off pin positioning system includes a photographic film punch and a double round hole off pin locator. The positioning method is as follows: first, align the front and back plates under the microscope; Punch two positioning holes out of the effective image of the base plate with a ¢ film punch. Take any one of the base plates with the positioning holes to compile the drilling program, and then you can get the data tape with the component holes and positioning holes drilled at the same time. Drill the component holes and positioning holes at one time. After the metallization holes of the printed board and ¢ pre copper plating, you can use the double round hole stripping locator for positioning and exposure.
3) Fixed pin positioning
The fixing pin is divided into two systems, one is to fix the photographic base plate and the other is to fix the printed board. By adjusting the position of the two pins, the coincidence and alignment of the photographic base plate and the printed board can be realized. After exposure, the polymerization reaction will continue for a period of time. In order to ensure the stability of the process, do not remove the polyester film immediately after exposure, so that the polymerization reaction can continue. Remove the polyester film before development.