Printed circuit board material is composed of fiberglass/plastic substrate, solder mask, copper and named ink.
Plastic substrate/fiberglass
Manufacturers can use flexible or rigid surfaces when fabricating PCBs. These two surfaces completely depend on the PCB design required for the project. Importantly, tough surfaces require polyamide fiberglass or FR4. At the same time, the flexible surface uses flexible materials such as high-temperature polyamide film. Some common non-conductive substrates for flex include polyamides, liquid crystal polymers, polyethylene, and polyester. Additionally, these substrates provide a non-conductive surface on which all conductive circuits run.
Copper wire
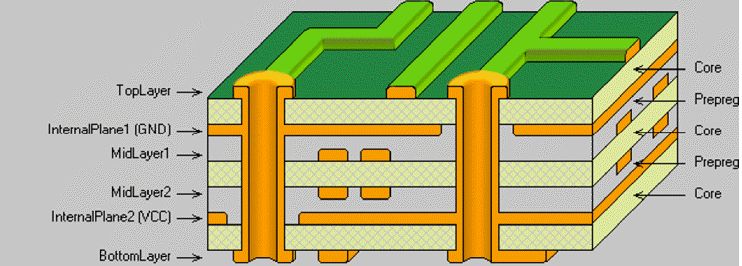
Copper wire has a very high conductivity. The plastic substrate used has thin copper traces laminated on all plastic sides. However, for multilayer PCBs, the structure is different. Multiple layers have alternating layers of copper that act as conductive material for insulating material.
Solder mask
Solder mask is a fluid that is typically applied to the outer layers of rigid printed circuit boards. Importantly, its job is to cover the copper pieces to keep them from oxidizing. Additionally, when all components are on the board, the fluid is retained and controls the flow of molten solder. When liquid solder flows off the surface, it has the potential to connect two adjacent circuits, creating a short circuit. It is worth noting that the solder mask has a typical green color. However, other colors such as blue, white, red, transparent can also be used.
Named ink
After applying the solder mask, the next step is to print barcodes, identification information and markings. These tags are nomenclature. Crucially, jargon facilitates accurate PCB assembly.
Type of printed circuit board
Below are the three most common types of PCBs with different material properties.
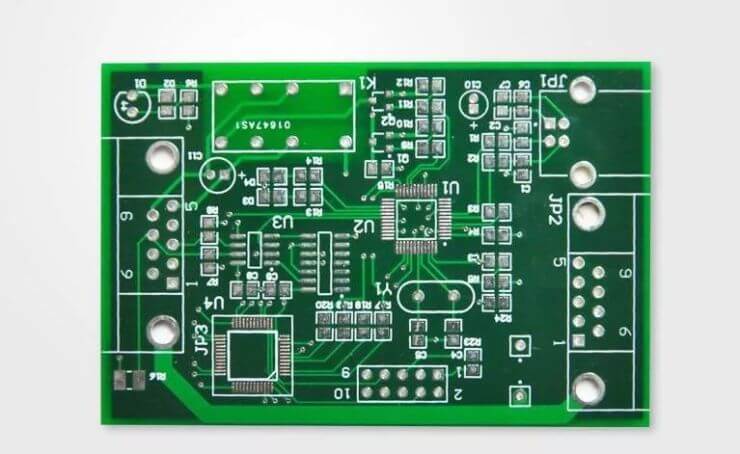
Rigid PCB
Rigid PCB types consist of a rigid fiberglass substrate. This feature makes PCBs cheap and practical. However, it is not flexible. Unlike flex PCBs, rigid PCBs are less expensive to produce. However, they are less general and thus difficult to adapt to certain device design practices.
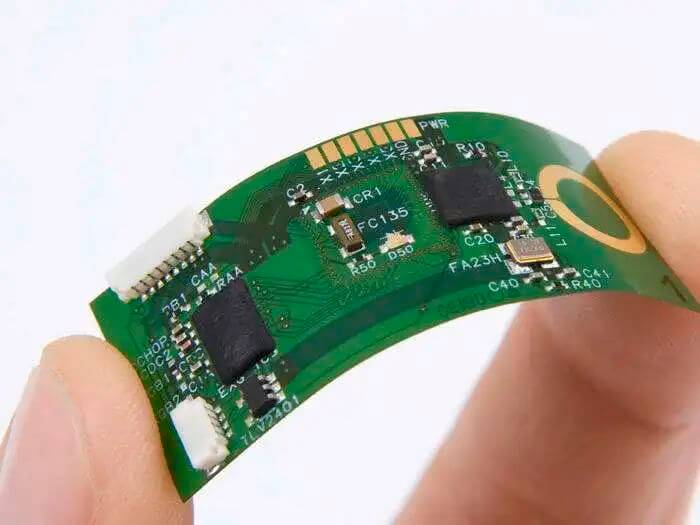
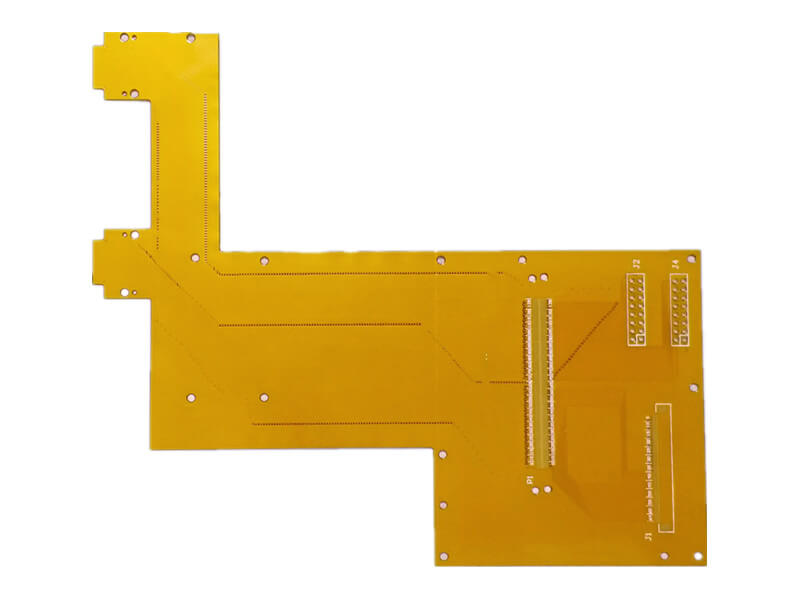
Flexible PCB
This PCB has an excellent flexible substrate. Importantly, this feature makes them versatile and can be installed in oddly shaped devices. These boards are adaptable and have no specific shape. Also, unlike rigid PCBs, flexible PCBs have higher heat resistance.
Rigid-Flex PCB
Rigid-flex PCBs reduce the weight and size of circuit boards by compactly containing the electronic interconnections within the board. Additionally, this PCB type is durable, strong, and flexible, combining the notable qualities of rigid and flex PCBs.

How to make PCB step by step?
The following steps can help guide you in developing a suitable PCB.
- The copper layer is chemically imaged and etched with small paths to connect the electronic components.
- The copper layer is laminated with an adhesive material that also acts as insulation.
- Plate and drill holes on the PCB to electrically connect all copper layers.
- The paths on the outer layers of the board are imaged and plated.
- Cover the board outline with solder mask, then print the naming marks.
- Machine the board according to the dimensions in the perimeter file.
After completing these steps, you can mount the components onto the PCB.