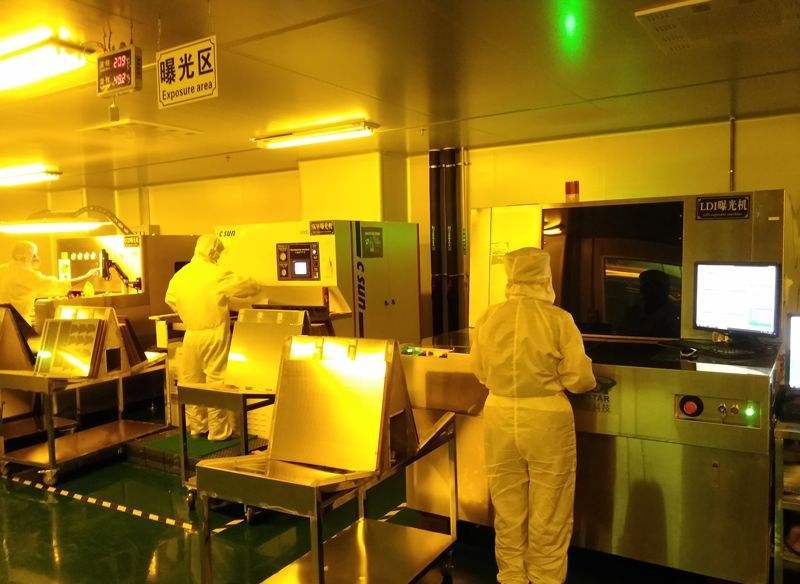
1. Cut
Cutting is the process of cutting the original CCL into boards that can be made on the production line
First, let’s look at some concepts
- Unit: unit refers to the unit graphics designed by PCB design engineers.
- Set: set refers to a graph that engineers put together multiple units to improve production efficiency and facilitate production. That is what we often call jigsaw puzzle, which includes unit graphics, process edges and so on.
- Panel: panel refers to the PCB manufacturer’s production, in order to improve efficiency, facilitate production and other reasons, put together a number of sets and add the edge of the tool board to form a board.
2. Inner Dry Film
The inner layer dry film is the process of transferring the inner layer circuit graphics to PCB board.
In PCB production, we will mention the concept of graphic transfer, because the production of conductive graphics is the fundamental of PCB production. So the process of graphic transfer is very important for PCB production.
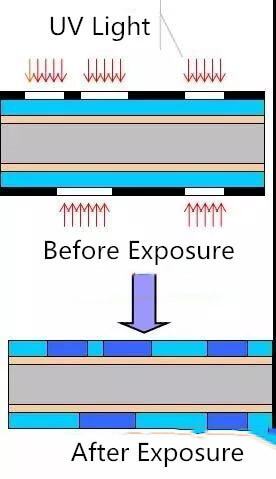
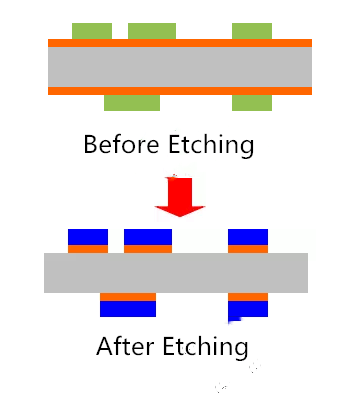
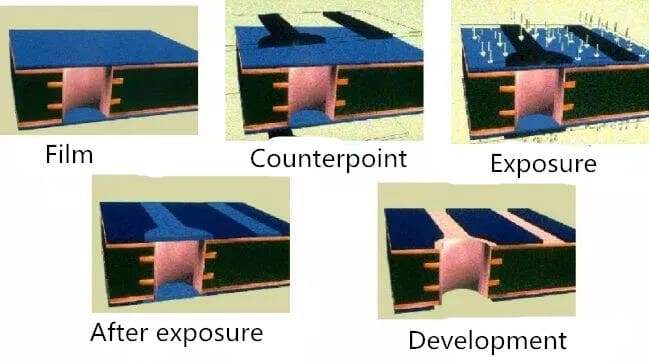
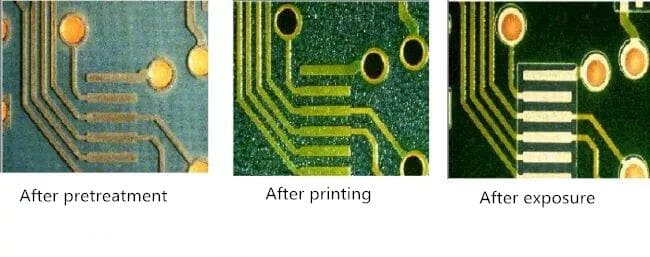
The inner layer dry film includes several processes, such as inner layer film, exposure development, inner layer etching, etc. The inner film is to apply a special sensitive film on the surface of the copper plate, which is what we call dry film. This film will solidify in light and form a protective film on the plate. Exposure development is to adhere to the film plate for exposure, the light transmission part is solidified, the light transmission part or dry film. Then after development, the uncured dry film is removed and the plate with the curing protective film will be etched. After the film removal process, the inner layer of the line graphics are transferred to the board. The whole process flow is shown in the following figure.
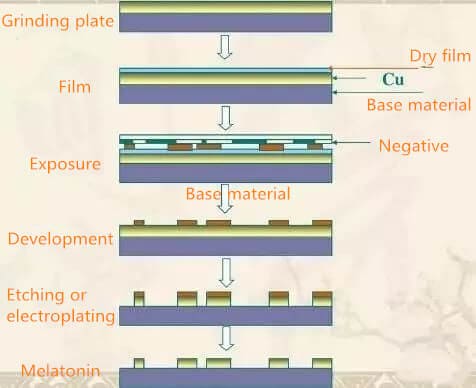
For designers, we mainly consider the minimum line width, spacing control and uniformity of wiring. Because the space is too small, it will cause the film to clip. And the film can’t fade out, which will cause the short circuit. The line width is too small and the adhesion of the film is insufficient, resulting in an open circuit. Therefore, the safe distance in circuit design (including line to line, line to pad, pad to pad, line to copper surface, etc.) must consider the safe distance in production.
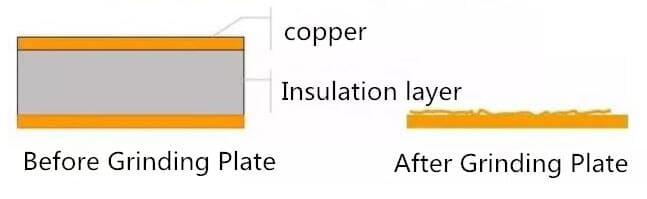
(1) Pretreatment: Grinding Plate
The main function of grinding plate: The basic pretreatment is to solve the problems of surface cleanliness and surface roughness. Remove oxidation, increase copper surface roughness, easy to film attached to the copper surface.
(3) Exposure
The negative film is aligned with the substrate of the pressed dry film. The negative image is transferred to the sensitive dry film by ultraviolet light on the exposure machine.
(5) Etching
After the unexposed dry / wet film is removed by the developer, the exposed copper surface will be exposed. The exposed copper surface will be dissolved and corroded with acid copper chloride to obtain the required circuit.
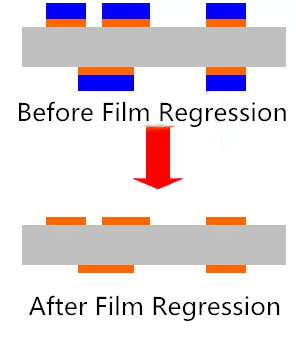
(6) Film Regression
Strip the exposed dry film on the copper surface with sodium hydroxide solution to expose the circuit pattern.
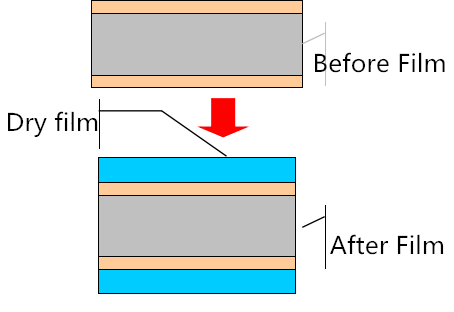
(2) Film
The treated substrate is pasted with dry film or wet film by hot pressing or coating to facilitate subsequent exposure production.
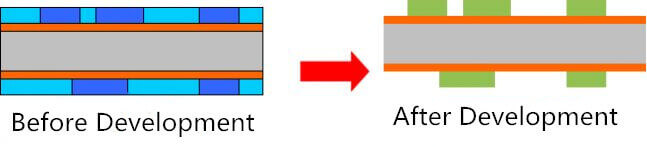
(4) Development
The unexposed dry / wet film is dissolved and washed out by the weak alkalinity of developer (sodium carbonate), and the exposed part is retained.
3. Browning
Objective: To form micro rough and organic metal layer on the inner copper surface and enhance the adhesion between layers.

Process Principle:
Through chemical treatment, a uniform organic metal layer structure with good adhesion characteristics is produced, which makes the surface of inner copper layer coarsen controlled before bonding. And it is used to enhance the bonding strength between inner copper layer and prepreg.
4. Lamination
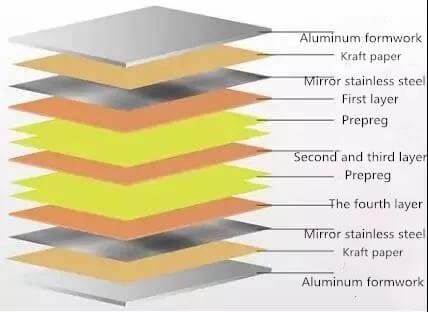
Lamination is a process of bonding each layer of circuit into a whole with the help of the adhesion of PP sheet. This kind of bonding is realized by the mutual diffusion and penetration of macromolecules on the interface, and then the interlacing is produced. The discrete multilayer board and PP sheet are pressed together into the required number of layers and thickness of multilayer board. In actual operation, copper foil, bonding sheet (semi cured sheet), inner plate, stainless steel, isolation plate, kraft paper, outer steel plate and other materials are laminated according to the process requirements.
For designers, the first thing to consider is symmetry. Because the plate will be affected by pressure and temperature during the lamination, there is still stress in the plate after the lamination. Therefore, if the two sides of the laminated board are not uniform, the stress on both sides is different, which causes the plate to bend to one side, which greatly affects the PCB performance.
In addition, even in the same plane, if the distribution of copper is uneven, the resin flow velocity of each point will be different, so that the thickness of the place with less copper cloth will be slightly thinner, and the thickness of the place with more copper will be slightly thicker.
In order to avoid these problems, the uniformity of copper distribution, the symmetry of lamination, the design arrangement of blind hole and so on must be considered in detail.
5. Drilling
The through hole is produced between the layers of the circuit board to achieve the purpose of connecting layers.
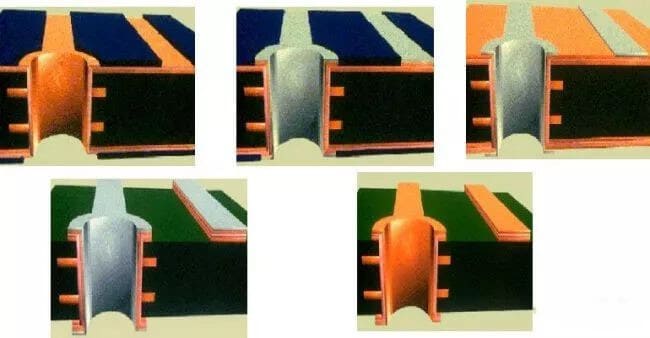
(2) Pate Plating
The PCB board just sunk out of copper is thickened to 5-8um in the surface and hole, so as to prevent the leakage of the substrate due to the oxidation and micro erosion of the thin copper in the hole before the graphic plating.
8. Outer Graphic Plating, SES
The copper layer of the hole and the line is added to a certain thickness (20-25um) to meet the requirements of the final PCB finished copper thickness. And the board surface of unused copper etched, showing useful circuit graphics.
10. Silk Screen Characters
The required words, trademarks or part symbols are printed on the board by screen printing, and then exposed on the board by ultraviolet radiation.
12. Forming
Cut PCB into required dimension by CNC molding machine.
6. Copper Plate Plating
(1) Copper Sinking
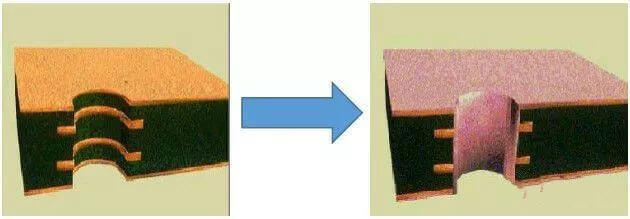
Copper sinking is also called chemical copper, the PCB board after drilling takes oxidation-reduction reaction in the copper sink, forming a copper layer to metallize the hole. So that the copper is deposited on the original insulating substrate surface to achieve the electrical communication between layers.
7. Outer Dry Film
The process is the same as that of inner dry film.
9. Welding Resistance
Welding resistance is also known as anti welding and green oil. It is one of the most important processes in the production of printed boards. It is mainly through screen printing or coating of welding resistance ink, and a layer of welding resistance is applied to the surface of the board. Through exposure development, the plates and holes to be welded are exposed. The welding resistance layer is covered in other places to prevent short circuit during welding
11. Surface Treatment
The solder ability of bare copper is very good, but it is easy to be oxidized by moisture in air for a long time. And it tends to exist in the form of oxide. It is unlikely to remain as the original copper for a long time. Therefore, surface treatment of copper surface is required. The basic purpose of surface treatment is to ensure good weld ability or electrical properties.
Common surface treatment: Tin spray, gold deposit, OSP, tin sinking, silver deposition, nickel palladium, electrohard gold, electric gold finger, etc.
13. Electrical Measurement
Simulate the status of the board, power on to check the electrical performance, whether there is open or short circuit.
14. Final Inspection, Sampling Test and Packaging
Check the appearance, size, aperture, thickness and mark of the plate to meet the customer’s requirements. Package qualified products into bundles, in order to make it easily to store and transport.