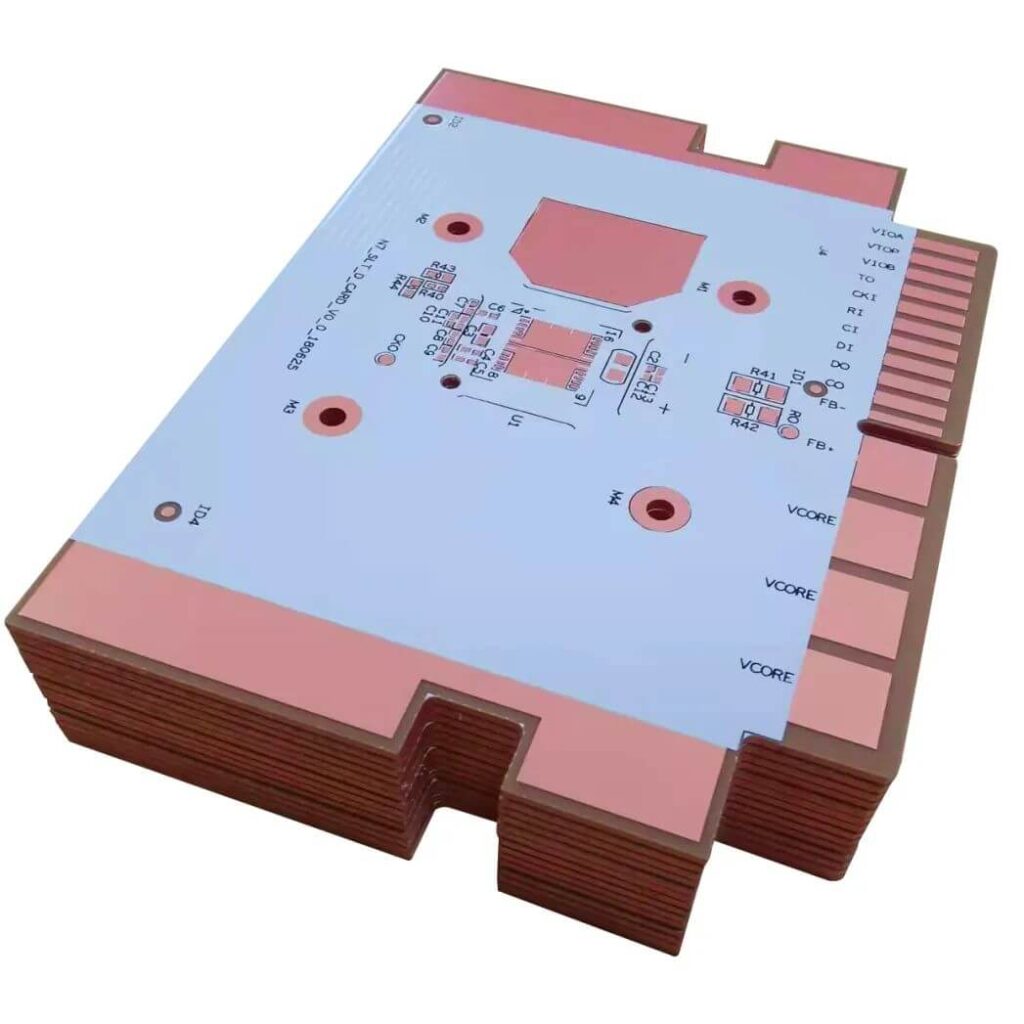
Printed circuit board (PCB) is an important electronic component and the support of electronic components. Because it is made by electronic printing, it is called “printed” circuit board.
In the production of electronic products, there will certainly be a production process of printed circuit board. Printed circuit boards are used in electronic products in all industries. It is the carrier of electronic schematic diagram that can realize the design function and turn the design into a physical product.
Before the emergence of PCB, the circuit was composed of point-to-point wiring. The reliability of this method is very low, because with the aging of the circuit, the rupture of the line will lead to the open circuit or short circuit of the line node. Winding technology is a significant progress in circuit technology. This method improves the durability and replaceability of the line by winding small-diameter wire around the column of the connection point. When the electronic industry develops from vacuum tubes and relays to silicon semiconductors and integrated circuits, the size and price of electronic components are also declining. Electronic products appear more and more frequently in the consumer field, prompting manufacturers to find smaller and more cost-effective solutions. So PCB was born.
PCB Production Process
Cutting – > pasting dry film and film – > exposure – > development – > etching – > film stripping – > drilling – > copper plating – > resistance welding – > silk screen printing – > surface treatment – > forming – > electrical measurement, etc
2 Layers PCB Production Process
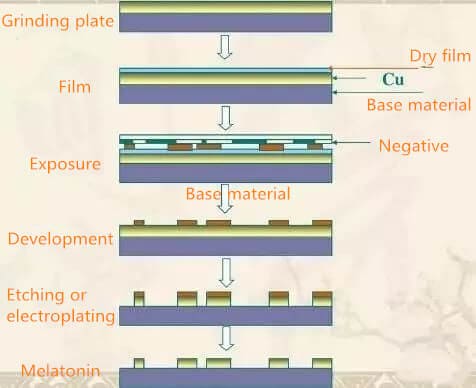
1. Cutting
Cutting is to cut the copper clad laminate into plates that can be produced on the production line. Here, it will not be cut into small pieces. First, assemble many pieces according to the PCB diagram, and then cut them into small pieces after PCB is finished.
2. Apply dry film and film
A layer of dry film is pasted on the copper clad laminate. The film is irradiated by ultraviolet light, and it will solidify on the board to form a protective film. This facilitates subsequent exposure and etching away unwanted copper(Generally speaking, the blue is the film, the yellow is the copper, and the green is the FR4 substrate.)
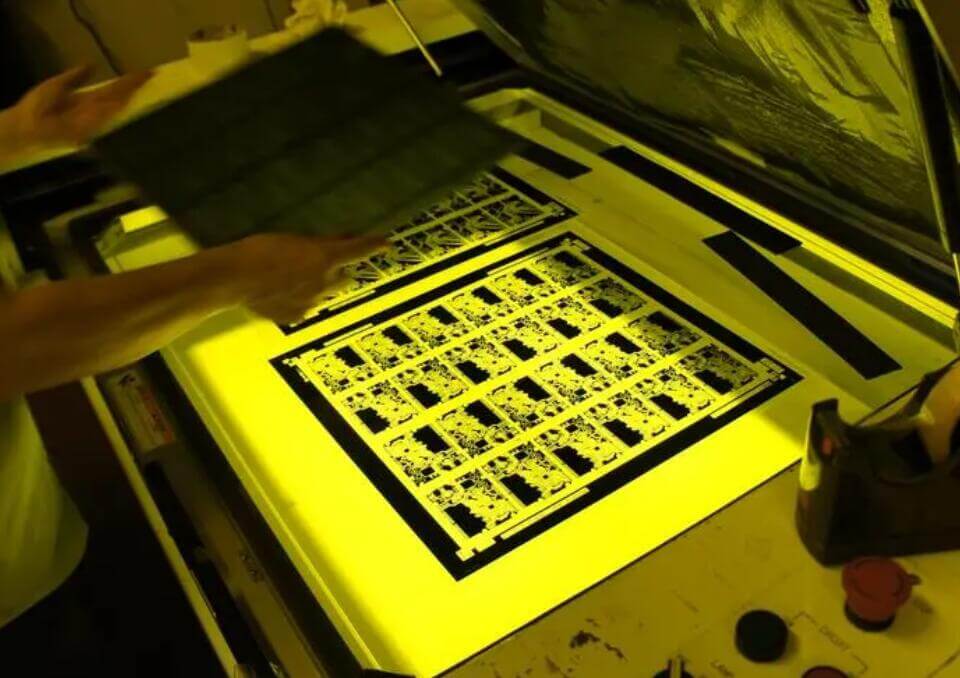
Then paste the film of PCB. The film is like a black-and-white negative of a photo, which is the same as the circuit diagram drawn on PCB. As shown in the figure below.
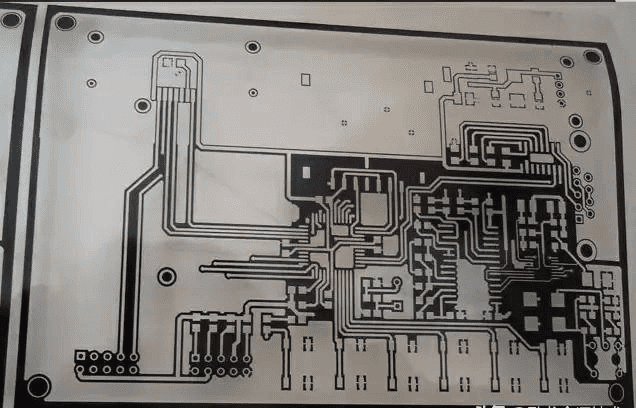
The function of film negative is to keep the place where copper needs to be left from ultraviolet light. As shown in the above figure, the white one will not transmit light, and the black one is transparent and can transmit light.
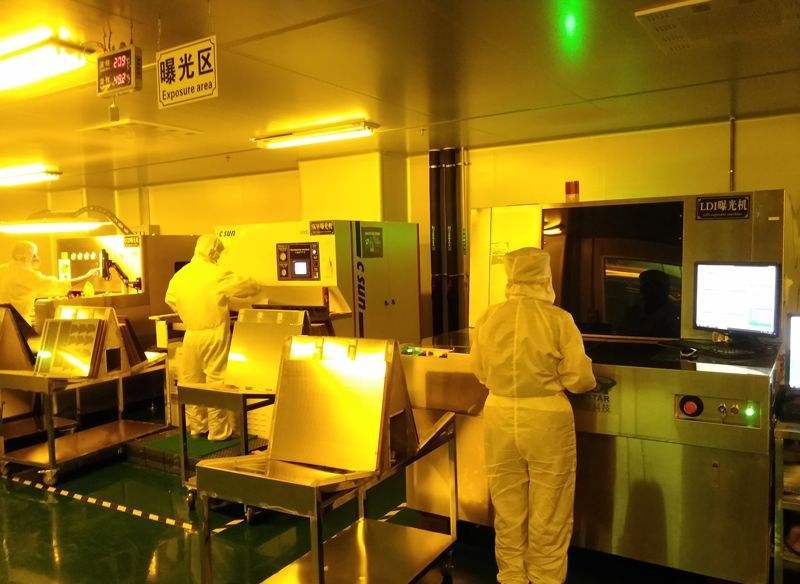
3. Exposure
Exposure is to irradiate ultraviolet light on the copper clad laminate attached to the film and dry film. The light shines on the dry film through the black and transparent place of the film. The place where the dry film is irradiated by the light is solidified, and the place where the light is not illuminated is the same as before. As shown in the figure below, after the blue dry film is irradiated by ultraviolet light, the front and back parts are cured. For example, the purple part is cured.
4. Developing
Development is to dissolve and wash the unexposed dry film with sodium carbonate (called developer, which is weakly alkaline). The exposed dry film will not be dissolved because it is cured, but will still be retained. It becomes the following figure. The blue dry film is dissolved and washed away, and the purple solidified film is still retained.
5. Etch
This step starts to etch the unwanted copper. The developed board is etched with acidic copper chloride. The copper covered by the cured dry film will not be etched, and the uncovered copper will be etched. Left the required wiring.
6. Film removal
The film removal link is to wash the cured dry film with sodium hydroxide solution. During development, the uncured dry film is washed off, and film stripping is to wash off the cured dry film. Different solutions must be used to wash the two forms of dry film.
So far, all the circuits that reflect the electrical performance of the circuit board have been completed.
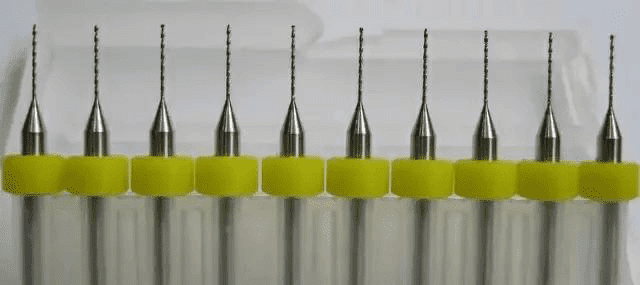
7. Drilling
This step starts drilling. Drilling includes punching pad holes and punched holes. The following figure shows PCB drill bit, which can drill holes with a minimum diameter of 0.2mm.
8. Copper plating
In this step, the wall of the pad hole and via hole is plated with a layer of copper and the upper and lower layers can be connected through the via hole.
9. Resistance welding
Resistance welding is to apply a layer of green oil on the non welding place, which is non-conductive to the outside world. This is through the screen printing process, apply green oil, and then, similar to the previous process, expose and develop the welding pad to be welded.
10. Silk screen printing
Silk screen printing is to print the component label, logo and some description words through screen printing.
11. Surface treatment
This step is to do some treatment on the pad to prevent copper oxidation in the air, mainly including hot air leveling (i.e. tin spraying), OSP, gold deposition, gold melting, gold finger and so on.
12. Electrical measurement, sampling inspection and packaging
After the above production process, a PCB board is ready, but the board needs to be tested. If there is an open short circuit, it will be tested in an electric testing machine. After this series of processes, the PCB board is officially ready for packaging.
Summary
The manufacturing process of PCB is very complex. Taking the four layer printed board as an example, the manufacturing process mainly includes PCB layout, core board manufacturing, inner PCB layout transfer, core board drilling and inspection, lamination, drilling, copper chemical precipitation of hole wall, outer PCB layout transfer, outer PCB etching and other steps.